- Spine Clinic
- About Our Spine Clinic
- C-Spine
- L-Spine
- Joint Clinic
- About Our Joint Clinic
- Knee
- Shoulder
- Hips
- Small Joint Clinic
- About Our Small Joint Clinic
- Hand
- Foot

+82-31-783-9623
+82-10-2783-6676
Our medical experts at BSH promise to provide honest and exceptional care.
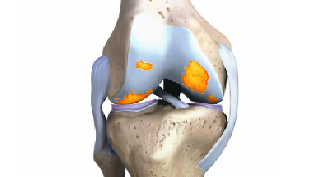
 Pain, swelling, and stiffness of the knee
Pain, swelling, and stiffness of the knee Sharp pain when doing particular motions
Sharp pain when doing particular motions If the area of damage expands and the pain persists, the problem can escalate to a more severe arthritis
If the area of damage expands and the pain persists, the problem can escalate to a more severe arthritis Simple X-Rays could reveal the progression of the arthritis, and through physical exams identifying the degree of swelling, the need for further testing can be established. MRIs and other more in-depth and invasive examinations can help make accurate diagnosis and proper course of treatment.
Simple X-Rays could reveal the progression of the arthritis, and through physical exams identifying the degree of swelling, the need for further testing can be established. MRIs and other more in-depth and invasive examinations can help make accurate diagnosis and proper course of treatment. Non-surgical treatment
Non-surgical treatment
This is for when the degree of rupture is relatively small and can be sufficiently treated non-surgically. Prolotherapy injection, Laser treatment, and rehabilitation exercise therapy will be conducted in phases.
 Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment
Simple Chondroplasty: chondroplasty is performed to remove and smooth damaged cartilage in the knee in order to lessen friction and allow healthy cartilage to grow.

Microfracture: Under the damaged cartilage, the surgeon rills tiny holes, encouraging blood circulation that lie inside the bone. The blood cells trigger the production of new cartilage. This is the most typical treatment for younger patients with smaller area of damage.

Autologous Chondrocyte Transplantation (ACI): This is a two-step procedure that takes several weeks to complete. First, healthy cartilage cells are arthroscopically harvested and grown in the laboratory for around five to six weeks. Then, the newly grown cells are arthroscopically implanted.

Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OAT): OAT involves transferring healthy graft (cartilage and underlying bone) from one part of the knee to the damaged area.

Stem Cell Cartilage Regeneration: Bone marrow stem cells are drawn from a patient’s pelvis and injected into the patient’s knee for cartilage repair. Another method is, doctors inject a fluid filled with placental stem cells into the damaged area. There are also stem cell treatments still in the research stages that use patient’s own stem cells from fatty cells and synovial membrane cells.